County Dublin topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
County Dublin
Dublin is a topographically varied region. The city centre is generally very low-lying, and many areas of coastal Dublin are at or near sea-level. In the south of the county, the topography rises steeply from sea-level at the coast to over 500 metres (1,600 ft) in just a few kilometres. This natural barrier has resulted in densely populated coastal settlements in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown and westward urban sprawl in South Dublin. In contrast, Fingal is generally rural in nature and much less densely populated than the rest of the county. Consequently, Fingal is significantly larger than the other three local authorities and covers about 49.5% of County Dublin's land area. Fingal is also perhaps the flattest region in Ireland, with the low-lying Naul Hills rising to a maximum height of just 176 metres (577 ft).
About this map
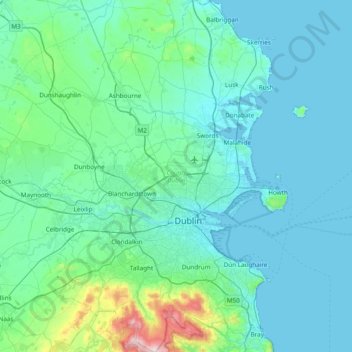
Name: County Dublin topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: County Dublin, Leinster, Ireland (53.17826 -6.54689 53.63471 -5.99450)
Average elevation: 71 m
Minimum elevation: -1 m
Maximum elevation: 733 m
Ireland trails, hiking, mountain biking, running and outdoor activities
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Easky
In Samuel Lewis's 1837 publication of A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland, Easky was described as having 6,124 inhabitants, of which 289 were in the village. Lewis noted that the village (made up of one long street) had petty sessions every fortnight and that Wednesday was market day. As well as other more…
Average elevation: 17 m
Blanchardstown
Blanchardstown was a predominantly rural area, with a small village, in western County Dublin, alongside the neighbouring district of Castleknock. Both areas shared a common history until well into the 19th century, when their development diverged. In A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland, published in 1837,…
Average elevation: 61 m
